Jaques A. C. Charles, químico famoso por seus…
(UNIRIO-RJ) Jaques A. C. Charles, químico famoso por seus experimentos com balões, foi o responsável pelo segundo voo tripulado. Para gerar o gás hidrogênio, com o qual o balão foi enchido, ele utilizou ferro metálico e ácido, conforme a seguinte reação:
Fe(s) + H2SO4(aq) → FeSO4(aq) + H2(g)
Supondo que tenham sido utilizados 448 kg de ferro metálico, o volume, em litros, de gás hidrogênio obtido nas CNTP (0 °C e 1 atm) foi de:
a) 89,6
b) 179,2
c) 268,8
d) 89.600
e) 179.200
Resolução
De acordo com a equação química, já balanceada, é produzido 1 mol de H2 para cada mol de ferro metálico consumido. Além disso, sabemos que 1 mol de qualquer gás a 0 ºC e 1 atm ocupa 22,4 L. Assim, temos:
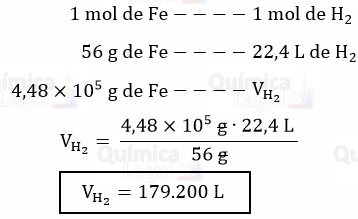
Lembre-se que: 1 kg = 1,0 × 103 g
Gabarito: LETRA E
Confira mais EXERCÍCIOS RESOLVIDOS de ESTEQUIOMETRIA.
Gostaria de ver mais RESOLUÇÕES COMENTADAS da UNIRIO?


